
This helps make you ready for a long, restful night of sleep.It would seem that sleeping is a simple activity - you power down, regenerate over several hours and wake up fully recharged. It can also help you feel relaxed and sleepy at night. It can help you feel awake and refreshed during the day. Getting regular, adequate amounts of sleep is important. It can lead to a decrease in performance, mood, and thinking. Abnormalities with the neurotransmitter dopamine may trigger sleep disorders such as restless legs syndrome.Įven losing just 1 hour of sleep over a few days can have an effect. Other neurotransmitters may work against you as you sleep. So if you study or learn new information in the hours before bed, "sleeping on it" can help you remember it. It then sets that information as you sleep. It seems to help your brain keep information gathered while you are awake. The neurotransmitter acetylcholine is at its strongest both during REM (rapid eye movement) sleep and while you are awake. They can even help you to remember things that you learned, heard, or saw while you were awake. Some neurotransmitters help your body recharge while you sleep. Melatonin makes you feel sleepy and ready for bed. This gland triggers the release of the chemical melatonin. But when darkness comes at night, the SCN sends messages to the pineal gland. Then the SCN triggers the release of cortisol and other hormones to help you wake up. The optic nerve in your eyes senses the morning light.
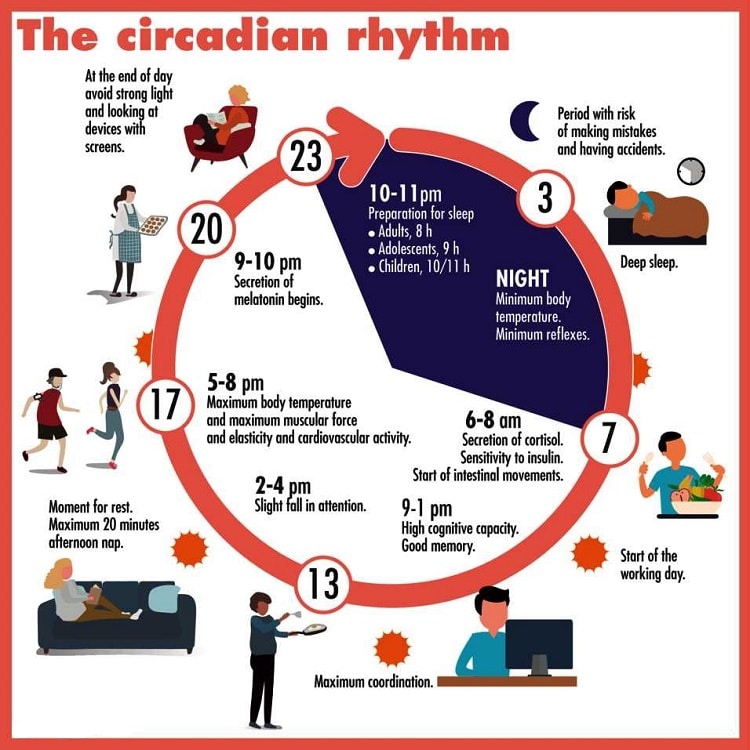
The SCN is sensitive to signals of dark and light. Your body’s internal clock is controlled by an area of the brain called the SCN (suprachiasmatic nucleus). Getting plenty of regular sleep each night can help to balance out these sleepy lows. Typically, most adults feel the sleepiest between 2 a.m. And you would be tired and ready for sleep at the end of the day.īut your circadian biological clock causes highs and lows of sleepiness and wakefulness throughout the day. If this process alone was in control of your sleep/wake cycles, in theory you would have the most energy when you woke up in the morning. With sleep/wake homeostasis, the longer you are awake, the greater your body senses the need to sleep. These are called sleep/wake homeostasis and the circadian biological clock.
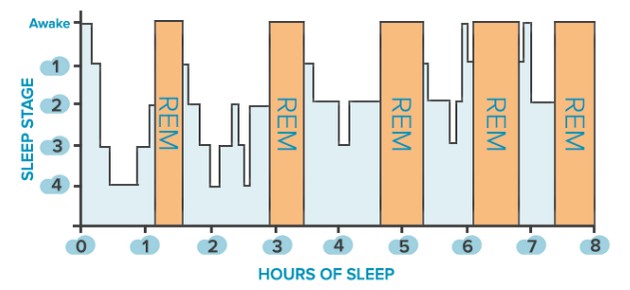
Two body processes control sleeping and waking periods. While you sleep, the chemical slowly dissipates. Caffeine promotes wakefulness by blocking the receptors to adenosine. Adenosine seems to work by slowly building up in your blood when you are awake. One chemical involved in that process is called adenosine. Other nerve cells stop the messages that tell you to stay awake. Neurotransmitters act on parts of the brain to keep it alert and working well while you are awake. These include norepinephrine, histamine, and serotonin. Nerve cells in the brainstem release neurotransmitters. Brain chemicals and sleepĬhemicals called neurotransmitters send messages to different nerve cells in the brain. These cycles are triggered by chemicals in the brain. How and when you feel sleepy has to do with your sleep/wake cycles. Later, your energy levels soar just in time for bed. Other times you toss and turn for hours before you slip into a fitful sleep.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
